Contents
Changing the way we’ve always done things can require some out-of-the-box thinking. In this article, we’ll go through five Augmented Reality enterprise use cases to showcase different ways large organizations have managed to incorporate AR technology, significantly reduce costs and boost revenue.
AR in Enterprise is on the Rise
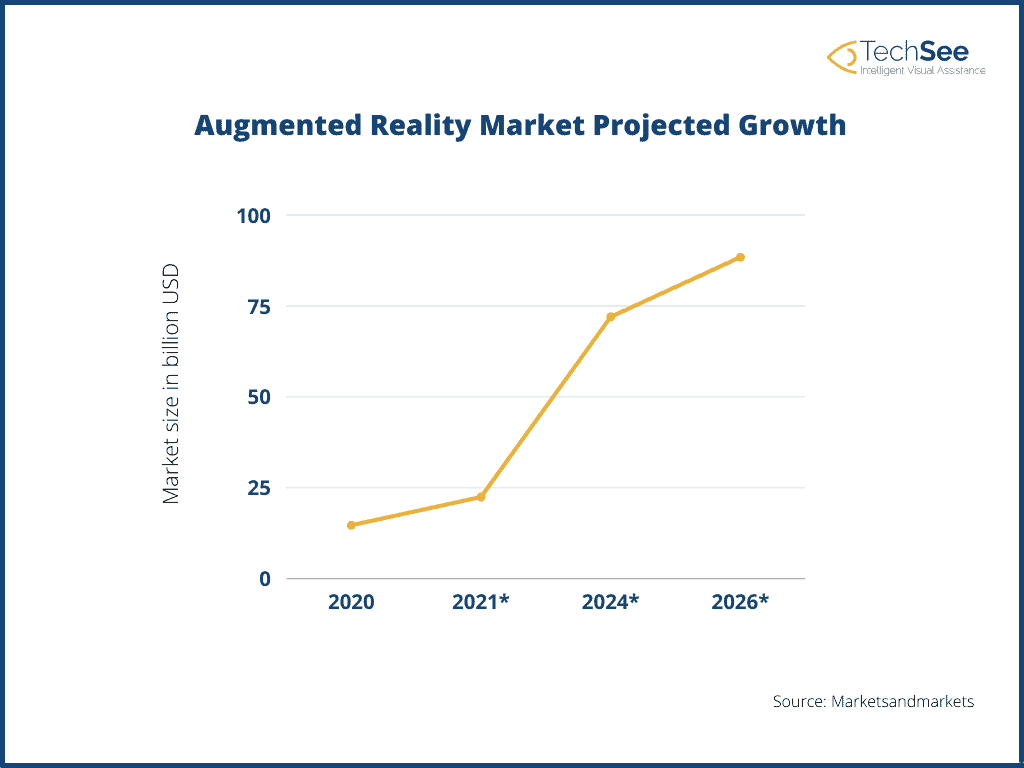
Augmented Reality (AR) is fast becoming an accepted part of our lives. A survey indicates that more than 68 million people in the US alone are already using AR, a number that is expected to grow rapidly over the next few years, with the global AR market predicted to be worth over $72B by 2024.
Why Do Enterprises Need Augmented Reality? 5 Use Cases
New Augmented Reality enterprise use cases are constantly being discovered. Business leaders should focus on those that offer real value and can make significant and lasting impacts on their organizations. We’ll discuss the following five examples of AR use cases:
- field services
- logistics
- training
- user manuals
- immersive analytics
Augmented Reality Field Service
AR technology is on its way to becoming firmly entrenched in the field service industry. The ability to utilize a hands-free collaboration tool powered by Augmented Reality, whereby graphical information is displayed over a physical environment, provides technicians with all the necessary data and instructions in real time.
Using a head-mounted device (HMD), a field technician can view a digital overlay of the equipment and see step-by-step instructions explaining how to proceed. If additional help is required, a remote technical expert can provide real-time visual guidance overlaid onto what the technician sees.
These use cases for Augmented Reality in enterprise are all about helping technicians quickly execute field repairs and avoid errors. These virtual field service tools have numerous benefits, including:
- delivering clear cost savings
- enabling faster repairs
- decreasing costly repeat technician visits by increasing First Time Resolution rates
- extending expert reach
- streamlining the training of novice technicians
Augmented Reality Applications for Warehouses, Logistics and beyond
AR technology empowers logistics staff by providing the right information at the right time and in the right place, an efficiency that is especially important to complex distribution networks. In warehouses, AR-enabled HMDs can be used to improve processes for:
- product picking and packing
- assembly
- inventory management
- assisting with the training of warehouse staff
For example, a worker can see task instructions overlaid on their HMD, which can be configured to assist with GPS navigation within the facility or with auto-reading of barcodes.
DHL Augmented Reality in logistics
With a DHL Trend Research Report estimating that drivers spend 40% to 60% of their days locating the correct boxes for their next deliveries, there is a clear need to find ways to slash this wasted time. For example, with AR in logistics technology, boxes could be overlaid with digital information that would highlight the package slated for the next delivery.
BMW has piloted the use of smart glasses at its Munich plant to display picking information in the worker’s field of vision, while barcode scans enable interaction with the warehouse management system. The pilot resulted in a 22% reduction in inventory identification time and a 33% reduction in errors over a typical eight-hour shift.
Augmented Reality in Training
AR-based hands-free devices are proving to be an engaging and efficient training tool, as they can overlay virtual tutorials onto wearable equipment to provide new personnel with quick, visual demonstrations. Clearly, it’s much easier to learn when viewing a digitally rendered 3D model than a 2D diagram. New staff can also learn on the job, rather than repeatedly checking the training manual. As such, the use of Augmented Reality in manufacturing training and other related fields is becoming increasingly popular.
Augmented Reality enterprise use cases like this are especially effective when it comes to highly complex tasks, such as aircraft assembly and maintenance. Boeing implemented an HMD for assembling wire harnesses for commercial aircraft, which helped the company cut production time by 25% and lowered error rates to nearly zero, while improving safety and enhancing the consistency of their SOPs. Japan Airlines also uses AR to provide supplemental training for engine mechanics and flight crew.
AR User Manuals
Replacing paper user manuals with immersive, visual AR instruction manual experiences helps customers navigate various steps including:
- initial product setup
- configuration
- troubleshooting
- routine maintenance
From the enterprise standpoint, AR instructions achieve better results, significantly alleviating the pressure on customer service departments. There are fewer calls to contact centers, less need to dispatch technicians to customers’ homes, and decreased return rates due to lack of customer product knowledge.
The most advanced AR user manuals are built around Computer Vision technology, which auto-identifies an issue and guides the customer toward self-resolution.
For example, IKEA’s AssembleAR app – built on Apple’s ARKit – utilizes the original diagrams in the paper instructions, but overlays them with animation and life-size references to simplify the assembly process. Nespresso enables users to scan their packaging and get step-by step coffee machine descaling instructions. And Hyundai’s app allows a motorist to point their smartphone at different parts of their vehicle, at which point AR instructions appear, overlaying information such as how to change the air filter, engine oil, or brake fluid.
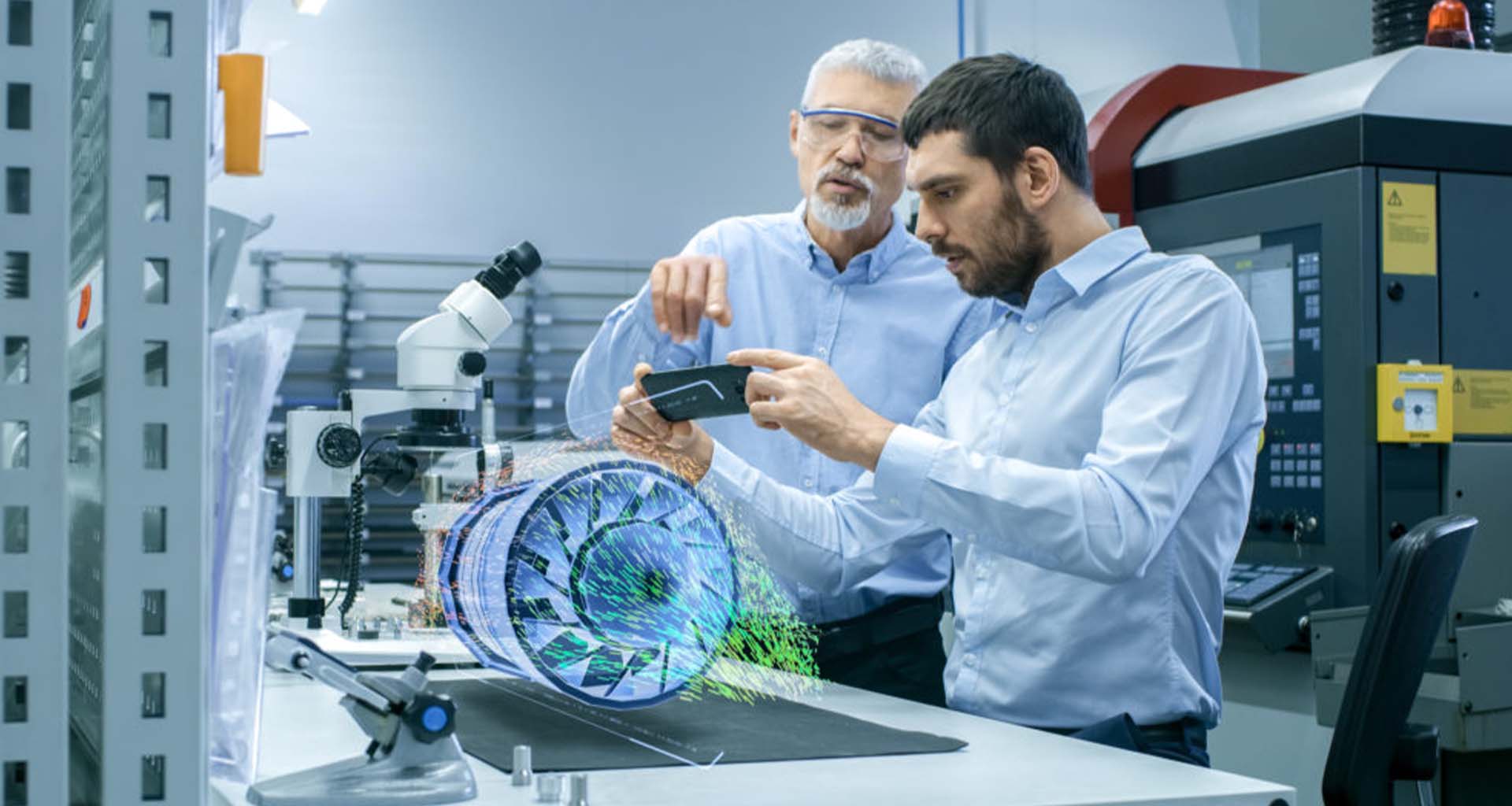
Immersive analytics
The benefits of data analytics for enterprise decision-making are well known. However, with growing volumes of data, 2D visualizations and manual processes limit companies’ abilities to detect data patterns and derive actionable insights. AR can provide new ways to visualize and make better sense of these complex datasets, providing real value to business leaders.
Immersive analytics is the combination of immersive technology and Machine Learning. Together, multiple departments can view, analyze and collaborate by visualizing data in 3D, with organizations such as IBM leading the way.
What To Learn
Gartner predicts that by 2022, some 70% of enterprises will be experimenting with immersive technologies for consumer and enterprise use and 25% will have deployed to production.
By combining virtual and real-world experiences, AR creates more engaging and interactive experiences, and is even more powerful when combined with Computer Vision AI capabilities. Enterprises should take note of the leading Augmented Reality enterprise use cases that can have a significant and immediate impact on almost all areas of a business and help the company on its journey toward successful digital transformation.