Contents
Over the past few years, deep learning has driven significant improvements in computer vision accuracy and performance. Deep learning, the most advanced form of AI, enables independent learning of massive data sets. Unlike classic methods in which a human expert needs to define features (rules and attributes), deep learning can learn straight from data without human intervention, with minor guidance (supervised learning) or without guidance at all (unsupervised learning). In some fields, deep learning achieves far greater results than classic computer learning methods.
Let’s take a look at how we can use some of these computer vision technologies to build our virtual technicians of the future.
Object Recognition
Object recognition is a technology that enables finding and recognizing objects within images or videos. Object recognition includes several tasks, such as:
- classifying that the image has a specific object
- localizing the object in the picture
- distinguishing the object from other objects
- identifying parts within the object.
Since 2015, deep-learning-based object recognition has achieved amazing results, with the error rate dropping below 5% (the human level). This means that in several fields, today’s machines can recognize objects even better than human beings can!
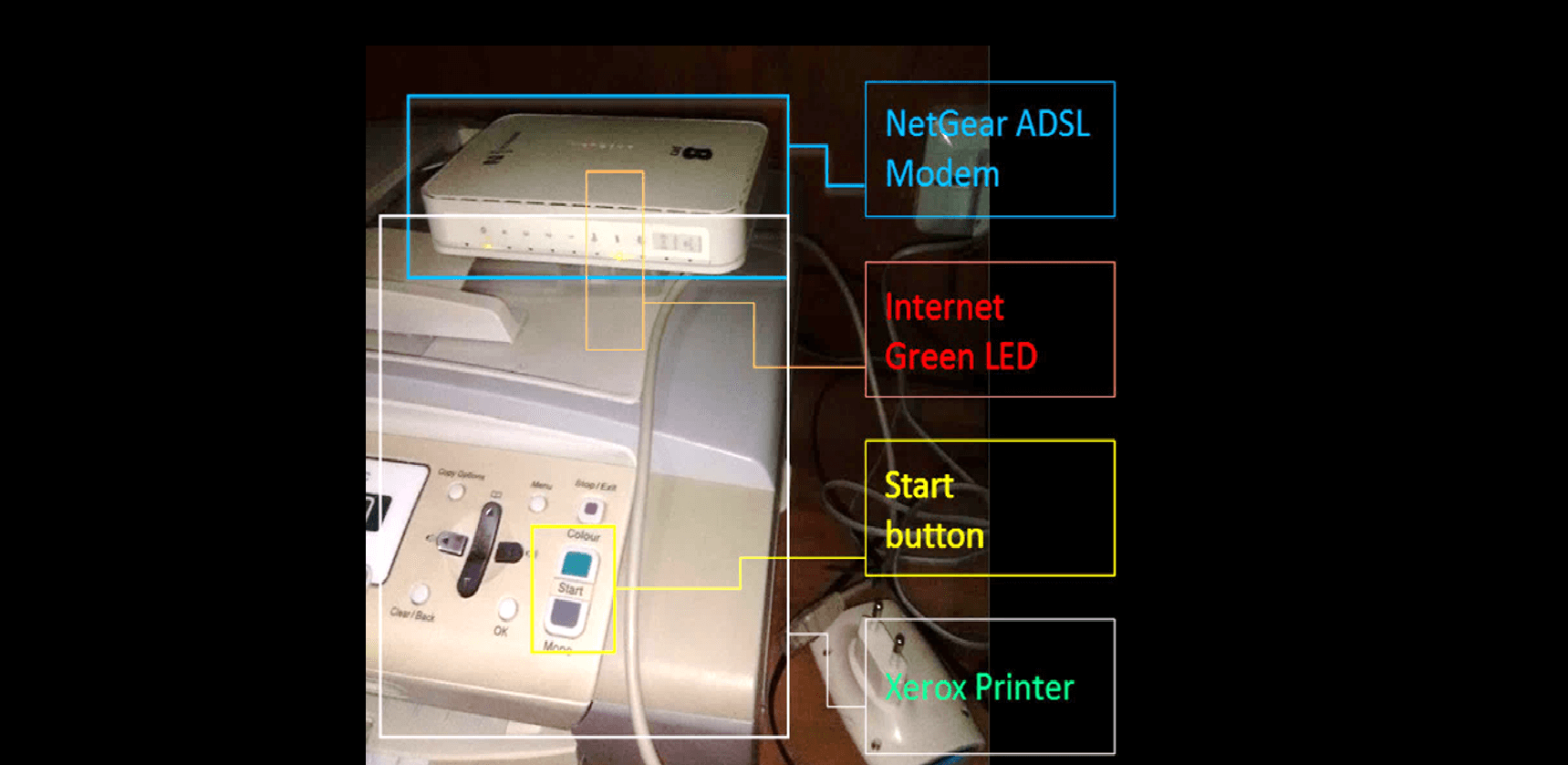
This incredible accuracy makes object recognition a core technology for the future computer vision-powered virtual technician. To diagnose an Internet connectivity problem, for example, a virtual technician needs to identify the router (and recognize the specific model), its parts (such as indication LEDs and back panel), and its cables; it also needs to localize all these objects to understand their context in order to diagnose the problem.
Image 1: Identifying Modem and Printer with Object Recognition
Image to text
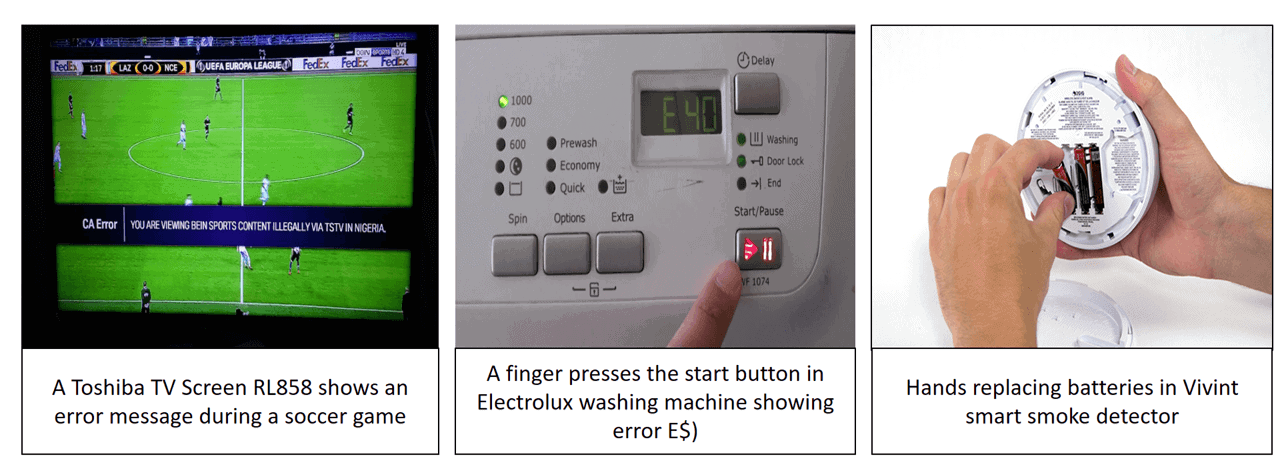
Image to text is the process of using ‘deep semantic alignments’ to create textual descriptions. The technology allows the network to describe what it sees on an image in a simple sentence.
A machine develops this capability by:
- recognizing objects and their locations within an image
- converting this information into text
- creating a meaningful contextual sentence to describe the image.
Using this technology, customers will be able to upload images of their equipment, after which a virtual technician with computer vision will automatically describe in a sentence what it sees. For example, “A DLINK 5323 modem with a red light and ADSL cable disconnected”.
Such a description may help a human agent in a contact center diagnose the problem more quickly. Alternatively, it could also help by using Natural Language Processing (NLP) to automatically retrieve textual explanations of how to solve a problem.
Image 2: Textual description for a TV screen issue
Visual Similarity
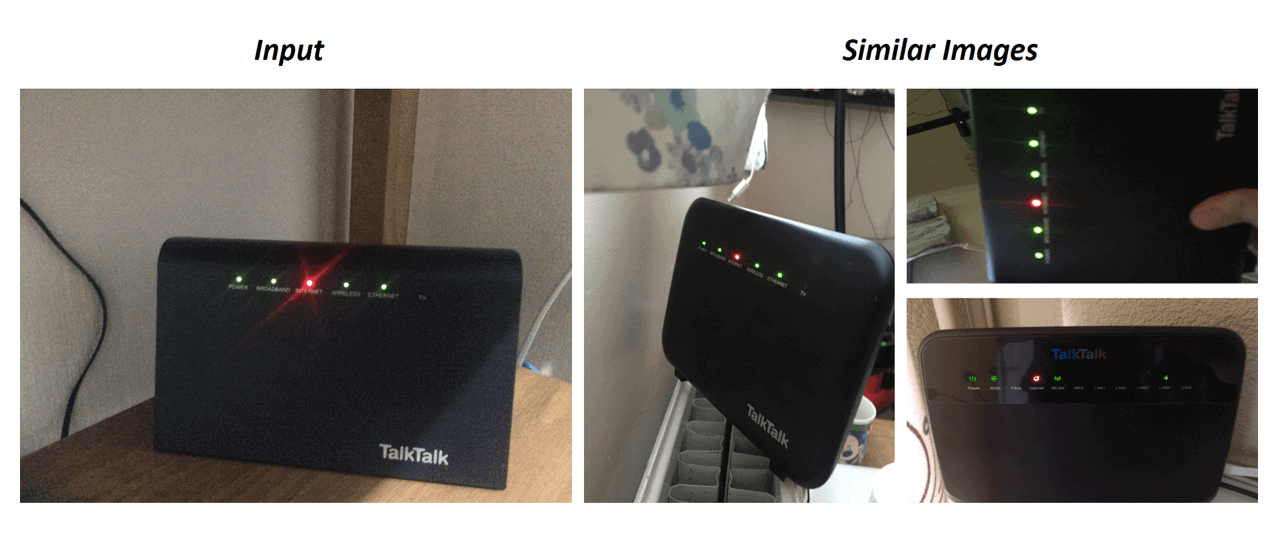
Visual similarity enables finding similar images to the image that is provided to the machine. This capability is essential, as sometimes it is hard to explain an image in words, and the easiest way to a solution starts with finding similar ones.
Visual search engines and websites such as Pinterest use visual similarity to provide their users with similar images (with related objects, colors, or patterns). Visual similarity will allow virtual technicians to use computer vision to take images of a technical issue and search for similar issues within massive visual data sets of captured technical cases.
Image 3: Finding similar issues with a specific router
Motion Detection
Motion detection is a technology that allows tracking moving objects in videos in real time. Motion detection is a fundamental capability in autonomous cars for ‘pedestrian detection’ capabilities; and in the security domain to identify moving persons detected by security cameras.
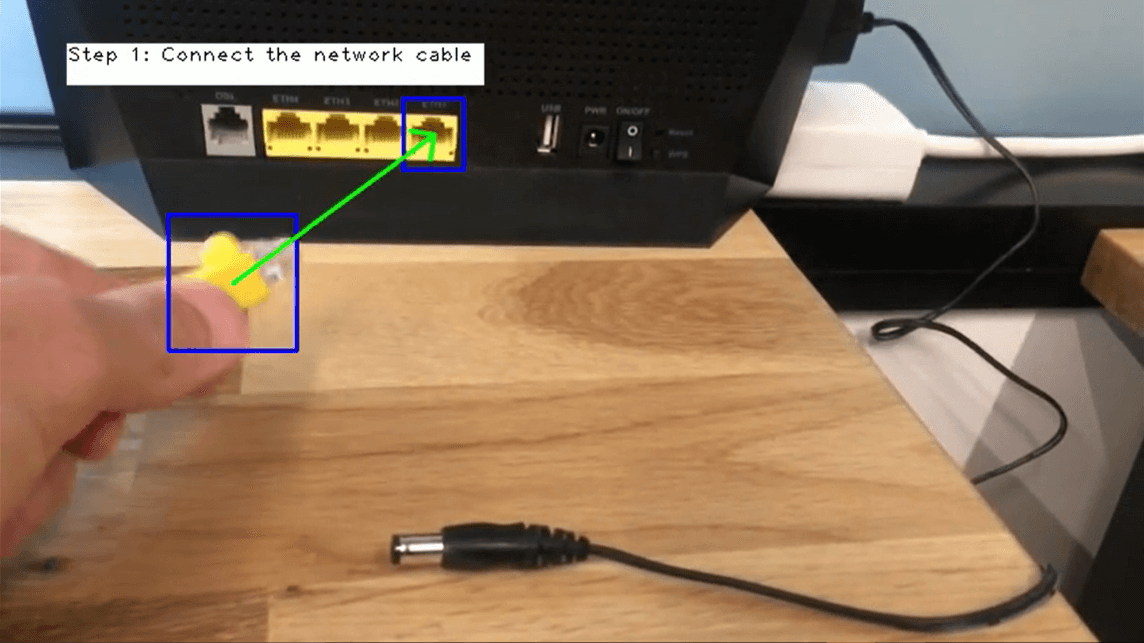
Motion detection is a key component of the future virtual technician, enabling it to provide instructions and feedback to customers in real time . For example, in order to instruct a customer on how to install a printer, a virtual technician needs to identify the customer’s hand movements and provide him with real-time instructions accordingly: for instance, “Now put the papers in the tray”, “Now hold the network cable. Not that one, the other one”.
Image 4: Motion detection in troubleshooting process
Face Recognition
Face recognition is recognizing faces within images. This is one of the most common tasks in computer vision. Deep learning has made significant improvements to machines’ facial recognition capability, especially in challenging lighting conditions, angles, and backgrounds.
“Good morning Mrs Brown,” chirps the virtual technician
With facial recognition, a virtual technician will be able to perform the critical task of recognizing customers, and greeting them accordingly:
“Hello Mrs. Brown, I see that you’re having trouble with your washing machine”.
Companies can also use facial recognition to offer biometric warranties, ensuring that customers get service for their devices without forcing them to save receipts and warranty documents.
Is Computer Vision the Way Forward for Virtual Technicians?
The progress of computer vision with deep learning will foster the creation of ‘artificial eyes’ for the virtual technician of the future, and help us, the consumers, manage the growing number of smart devices that we’re setting up in our smart homes.
In our next article in this series, we will detail how we can actually use computer vision to bring the virtual technician of the future into the present with object recognition.