Contents
The value of augmented reality in field service has been clearly proven, and an increasing number of field service organizations are beginning to incorporate AR technology. In fact, the field service industry is one of the market leaders where it comes to practical AR implementation. But with different options available, how should a field service organization decide which augmented reality solution is best for them?
The Value of AR in Field Service for Your Business
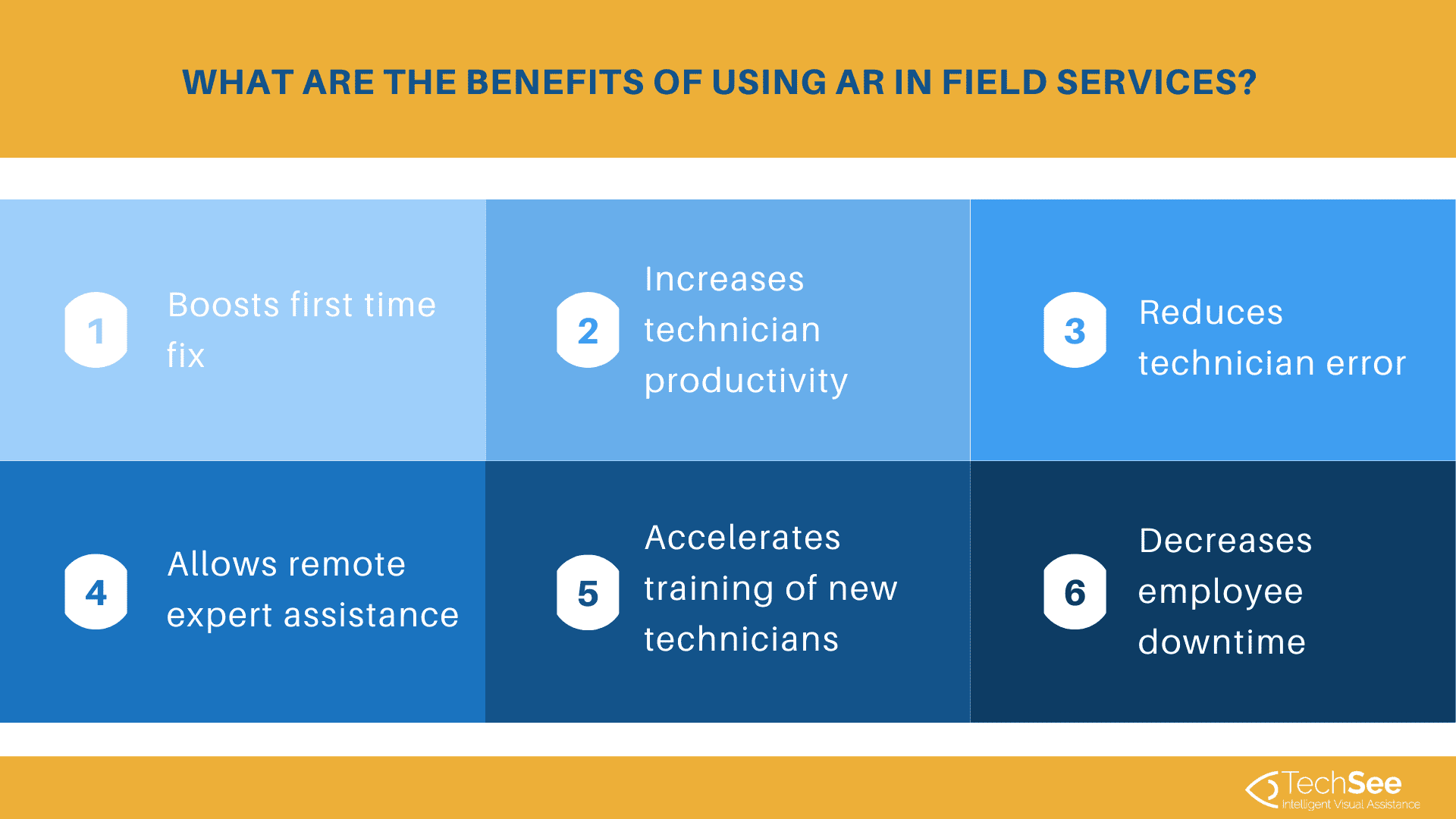
The ability to overlay visual information onto images of physical objects is transforming the field service industry in various ways, across the main operating models. AR technical guidance support technicians in repair execution, consultation, knowledge sharing, and better preparation to expedite a resolution process.
AR virtual tools deliver clear cost savings, reduce travel time, decrease employee downtime, extend expert reach, and accelerate the training of new technicians.
AR Smart Glasses vs AR Mobile Phone App: Main Field Service AR Tools
Augmented reality in field service is delivered primarily via smart glasses or mobile phones. Both offer high quality visual support for technicians and each delivery method has its own advantages and limitations.
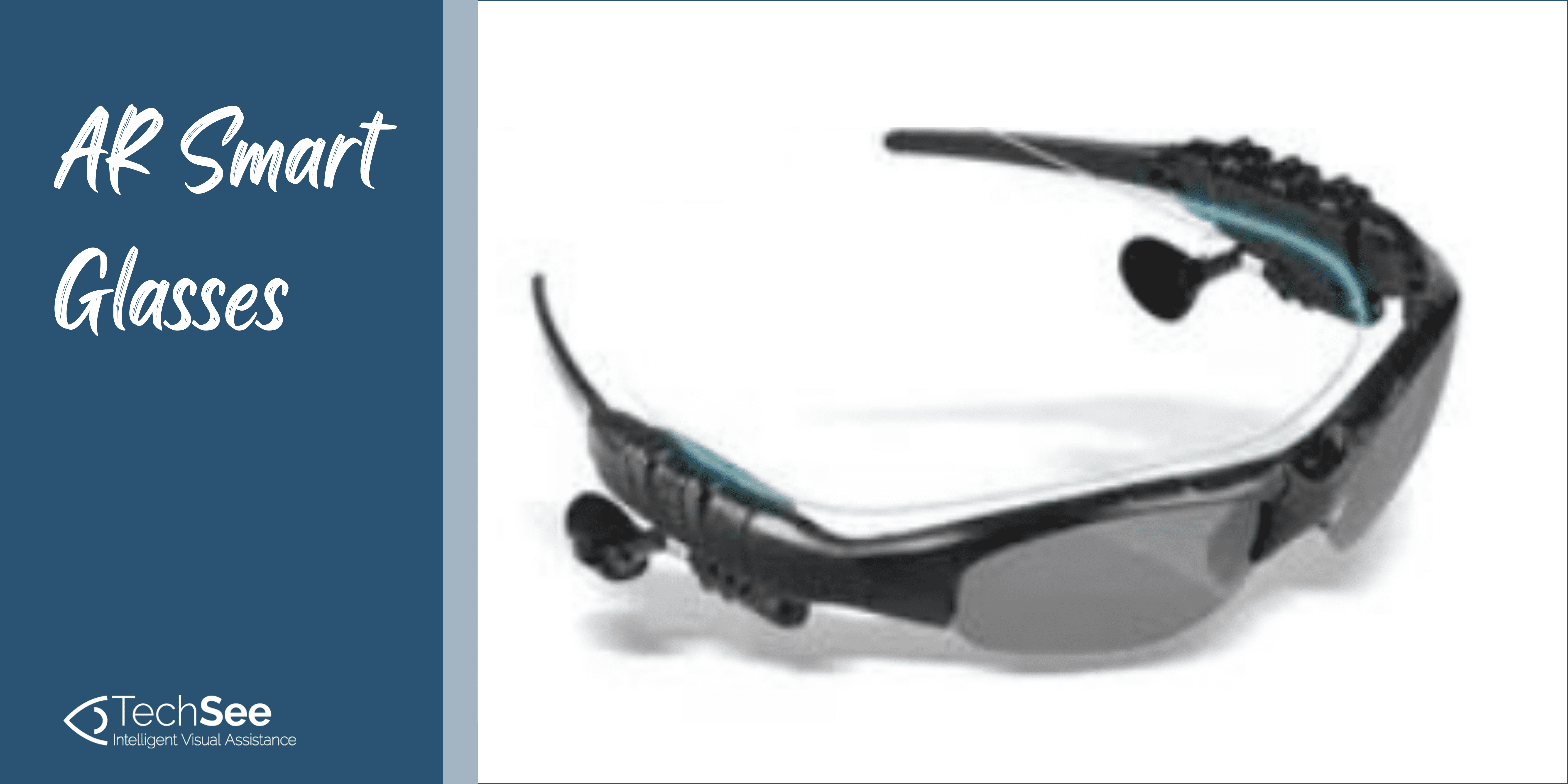
AR Smart Glasses (Head-Mounted Devices)
Wearable AR devices such as these smart glasses offer users a hands-free experience. Worn like eyeglasses, they enable the technician to view and interact with video and digital content, enhancing their view with computer-generated information.
AR Mobile Phone
Screen-based AR field service systems are designed to provide mobile phone or tablet users with interactive video and digital content, applied on top of the image of physical reality. These applications utilize a standard mobile device’s existing components such as the camera, GPS, and touch screen elements to enhance the user’s view.
AR Smart Glasses vs AR Mobile App: Which Is Best for Your Field Service?
Both augmented reality smart glasses and AR on mobile phones offer benefits for enterprises. Which situations are each solution most suitable for?
Augmented Reality Smart Glasses
- If you need completely hands-free operation. If the technician requires both hands for safety purposes, such as for climbing, or if gloves will be worn in the field and swiping a screen is not a possibility, augmented reality smart glasses have a clear advantage.
- For highly complex service work. In scenarios involving long sequences of actions, such as the one implemented by Boeing for assembling wire harnesses for commercial aircraft, smart glasses have the advantage since the technician can keep their eyes on the device and instructions at all times. This ability has been proven to drive 15% improvements in the time it takes to perform a long sequence of actions on a piece of machinery.
- If service is provided in a fixed location. In factory settings, or in other facilities offering full control over the environment, technicians using smart glasses can rely on continuous network connectivity with high levels of bandwidth, controlled lighting, and a safe location to store the devices when not in use.
- If 3D AR is required. Another benefit of smart glasses is the 3D AR experience they offer; in most cases they present a more accurate overlay which is important in situations where total precision is required.
AR Mobile App
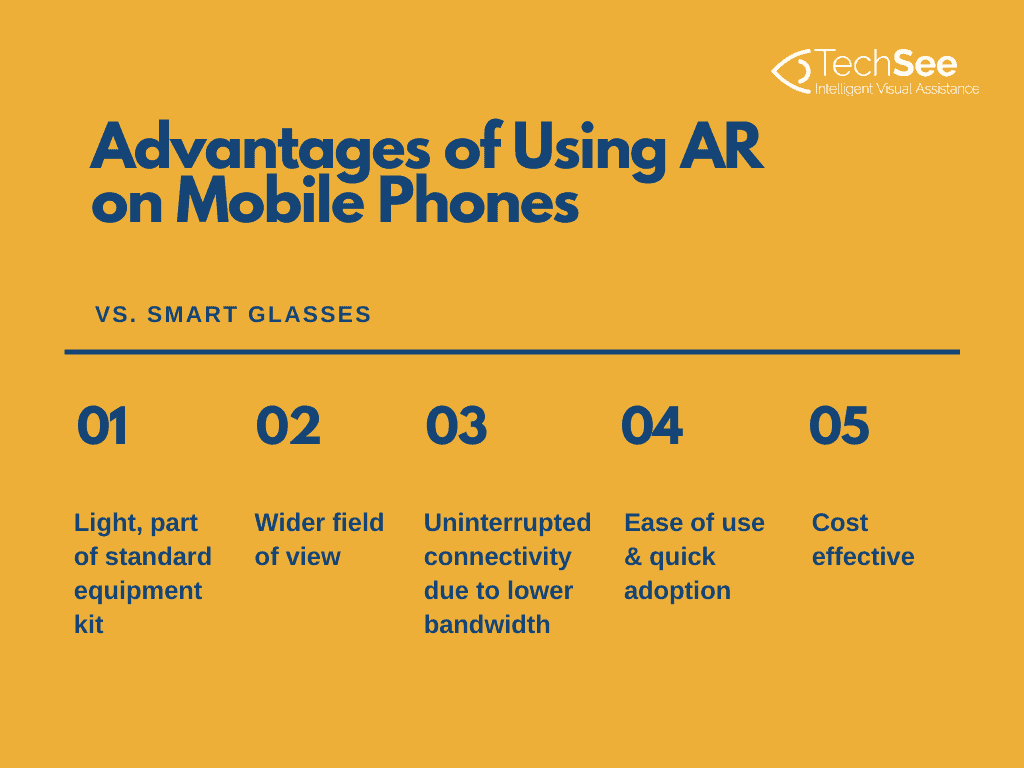
- If less (equipment) is more. When technicians are dispatched, they are often carrying numerous tools and spare parts, as well as their regular mobile phone. Smart glasses are often fragile and represent yet another piece – or several pieces – of equipment that must be packed in the technician’s toolbox. Using AR functionality on the technician’s phone, on the other hand, is simple and fast.
- In dynamic scenarios. In situations where conditions can change rapidly, or when interaction with a customer may be required, mobile devices make it easier for the technician to interact with their environment.
Smart glasses can disconnect the technician from reality by keeping him focused on a very narrow field of view. In addition, in hazardous situations, smart glasses may create a distraction or even pose a danger. Allowing a wider field of view where the technician can experience both the physical reality and the AR overlay can offer an advantage in quickly solving the problem at hand and ensuring technician safety.
- For uninterrupted access. Smart glasses are limited by two factors. They have a short – and sometimes unreplaceable – battery life and they usually require a consistently high level of connectivity. AR solutions for mobile devices often have more flexible data requirements and a significantly longer battery life.
- For ease of use and quick adoption. Everyone knows how to use a smartphone, with tap and swipe now second nature. However, the use of smart glasses is still an acquired skill. Some require the technician to swipe the empty space in front of their face, while others require them to tap or scratch the arm of the glasses. Voice-activated solutions are available for both options and make things easier, but mobile devices are currently the clear winner in the UI (user interface) stakes.
- If price is a factor. Screen-based applications integrate with the technician’s existing mobile device (phone, tablet, etc.), and are significantly more cost-effective when deploying to a large workforce. It also makes it easier to deploy as a pilot initiative to a limited number of users, enabling the organization to evaluate its true value before investing in expensive hardware.
| Criteria | Smart Glasses | Mobile Devices |
|---|---|---|
| Hands free | Yes, no toggle necessary | Limited, must toggle between task and device |
| Field of view | Limited | Unobstructed |
| Mobility | Heavy, cumbersome, requires unpacking and packing, sensitive | Light, part of standard equipment kit |
| Battery life | Short, often not replaceable | Longer lifespan, additional or bigger batteries available |
| Connectivity requirements | Uninterrupted, high bandwidth | Can manage with lower bandwidth or interrupted coverage |
| Ability to communicate with customers | Limited | Natural |
| AR quality | 3D | 2D |
| Maturity | Immature, less stable | Mature, in wide use |
| Price | High cost deployment | Affordable deployment |
AR Glasses or Mobile App – In Summary
The implementation of augmented reality in field service is radically changing the dynamics of service operations, enabling organizations to boost productivity and cut costs. AR-supporting smart glasses and mobile devices both provide field technicians with the innovative tools they need to complete their repair and service tasks more quickly and efficiently.
Both are set to play a key role in the maintenance and operation of equipment across industries, and change how field service teams train new staff. The type of AR device an organization chooses to implement should be determined based on specific criteria and reflect the individual needs and requirements of the organization and its technicians.